Explainable Spatio-Temporal GNNs
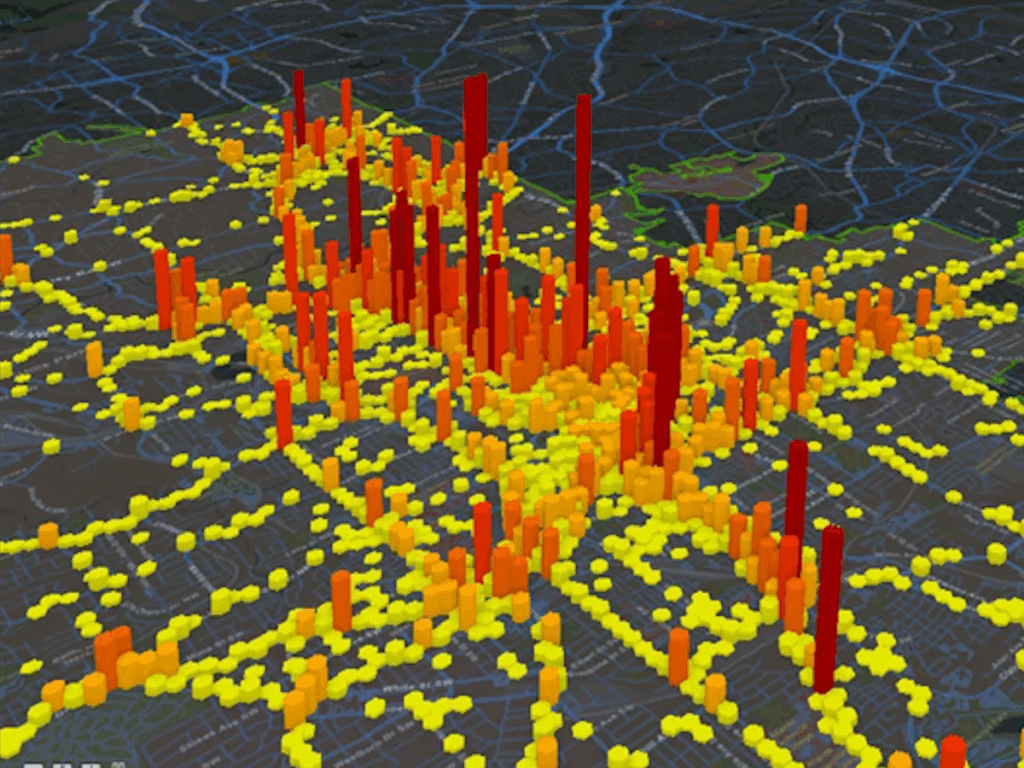
Spatio-temporal graph neural networks (STGNNs) have gained popularity as a powerful tool for effectively modeling spatio-temporal dependencies in diverse real-world urban applications, including intelligent transportation and public safety. However, the blackbox nature of STGNNs limits their interpretability, hindering their application in scenarios related to urban resource allocation and policy formulation. To bridge this gap, they propose an Explainable Spatio-Temporal Graph Neural Networks (STExplainer) framework that enhances STGNNs with inherent explainability, enabling them to provide accurate predictions and faithful explanations simultaneously.
Graph Neural Network-Based Anomaly Detection in Multivariate Time Series

In this presentation, a novel approach to anomaly detection using Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) is introduced. This method models multivariate time series as a graph, learns sensor relationships and detects anomalies by identifying deviations from these learned patterns. By capturing both temporal dependencies and sensor interactions, proposed approach enhances anomaly detection, offering superior performance compared to traditional techniques.
Large Language Models

Large Language Models (LLMs), renowned for their prowess in natural language processing, have emerged as powerful AI systems. Foundation Models, a broader category encompassing LLMs, are characterized by their broad capabilities and adaptability to diverse tasks through fine-tuning. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) excel at processing and learning from graph-structured data by iteratively aggregating information from neighboring nodes. The synergy between these models holds immense potential. LLMs can enhance GNNs by providing richer node embeddings, capturing complex semantic relationships, and enabling more effective reasoning on graph data. Conversely, GNNs can leverage the powerful pattern recognition abilities of LLMs to improve their understanding of complex graph structures and enhance their performance on tasks involving relational reasoning
GraphAny
GraphAny is a groundbreaking foundation model for node classification on any graph, addressing the limitations of existing models that struggle to generalize across different graph structures and feature spaces. This innovative approach leverages a novel architecture consisting of LinearGNNs and an attention mechanism that learns to combine their predictions, enabling effective inference on new graphs without the need for retraining. By learning attention scores for each node based on entropy-normalized distance features, GraphAny demonstrates remarkable generalization capabilities, surpassing traditional methods in various node classification tasks.
Temporal Graph Embedding
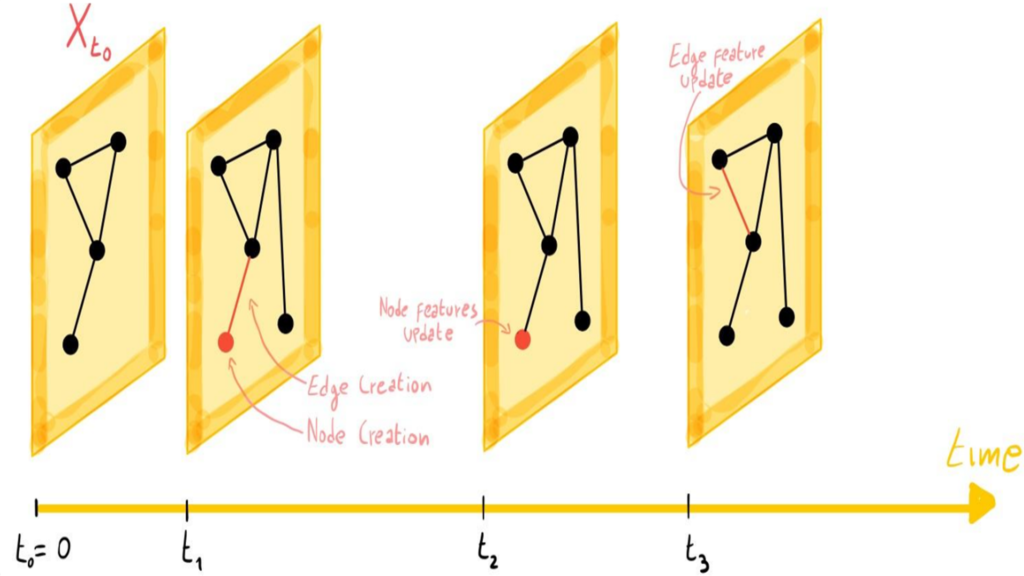
Temporal Graph Embedding is a technique that aims to represent nodes and edges in a dynamic graph within a low-dimensional vector space, capturing their temporal evolution. By learning meaningful representations, these embeddings enable various downstream tasks such as link prediction, anomaly detection, and community discovery in time-varying networks. These models effectively capture the evolving relationships between entities over time, providing valuable insights into dynamic systems like social networks, citation networks, and financial transactions.

